We have all been compelled to consider remote learning as a legitimate alternative to on-campus teaching. For the advocates of technology integrated learning (fully online or blended) – who have chipped away at good designs for learning with educational technologies – it was a triumph and a long time coming. Educators who were yet to be convinced about the possibilities of online or digital learning, quickly adopted remote learning opportunities out of necessity. How did we achieve such a feat? Be it new ways of delivering or facilitating learning, we all had to build our capacity to do so in a short period of time. Welcome the #pivotonline movement.
#pivotonline resources:
Twitter; #pivotonline
AACE: Stories from the field ebook
Linkedin group: Moving HE teaching online
Online Learning Consortium: Faculty Playbook
Coursera: Learning to teach online
OpenLearn: Take your teaching online
Youtube: Open teach
University of Auckland: Remote learning
Googledoc: Hybrid learning; Higher Ed Guidance
Public network: Keep teaching
Blog: Edvisor community
Global support group: #OER4Covid
Asian Journal of Distance Education: Diverse perspectives
EDUCAUSE: Teaching continuity
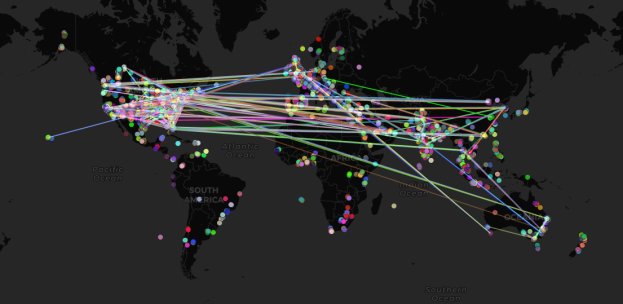
#Pivotonline is my doctoral research playing out in real-time, educators networking to build their capacity for teaching with technologies. If we consider a platform like Twitter, we can see how these networks form and flourish – with short and long term connections. The image here is of the publicly available Tweets using pivotonline hashtag. What do these connections mean and what value do they hold for the educators involved? What benefits and challenges did these new ways of learning present for our students?