Related project: Technology for equitable learning opportunities and design
(Learning Enhancement Grant 2019-2020)
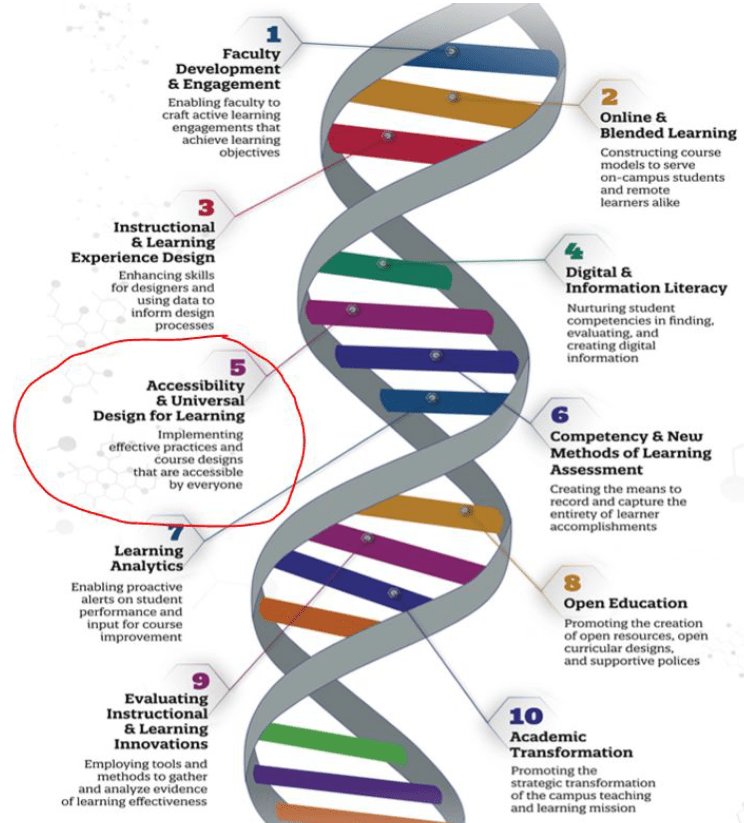
What can technology do to create barriers to learning? Seems like plenty… EDUCAUSE in its 2019 elearning initiative, identified accessibility and Universal Design for Learning (UDL) as a key teaching and learning issue. Our presentation (2019 Scholarship of Technology Enhanced Learning conference) on the core consideration for inclusivity in design – audience, tools, content and legislation – opened up some interesting discussions. Many at times we make assumptions about our learners and their digital skills; accessibility and usability of tools; content creation quailty (re-packaging rather than re-purposing) and the law (accessibility standards). How can we ensure that our learning designs and content facilitation through technology offers equitable learning experiences?
What do our learners find useful?
Even though students in Australia and New Zealand report high levels of digital activity than UK students, they agree that technology can have negative impacts on their studies. Unless designed well and integrated into the core learning outcomes, these learners rather not have digital technologies used in their courses (Beetham, Newman & Knight, 2019).
What tools are useful?
The use of digital technologies don’t always lead to creative, collaborative, participatory and hyper-connected practices. Henderson, Selwyn and Aston (2017) indicate that rather these are the activities, practices and processes that students feel compelled to undertake in order to ‘do’ university.
...many of the reportedly ‘educational’ benefits of digital technology…are more accurately described as concerned with the ‘logistics’ of university study rather than matters related directly to ‘learning’ per se.
Henderson, Selwyn & Aston (2017)
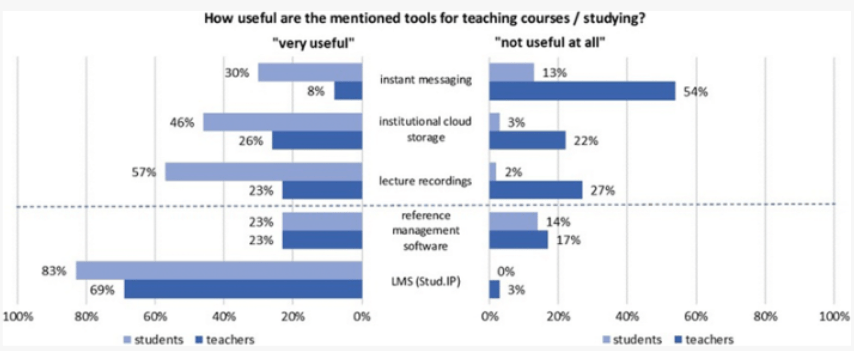
Bond, Marín, Dolch, et al. (2018) reported differences in how learners and teachers perceive the usefulness of tools such as lecture recordings, the learning management system (LMS) and reference management systems. For example, close to a quarter of all teachers they researched, thought lecture recordings were not useful but close to 50% of the students found them useful.
What guidelines apply for accessible and intuitive content development?
Web content accessibility guidelines (WCAG 2.1/W3C)
European Union accessibility act
Web accessibility guidelines (Australia)
Proposed changes to web standards (New Zealand)